Reading Time: 3 mins
What are adhesive systems, and why are they essential in operative dentistry?
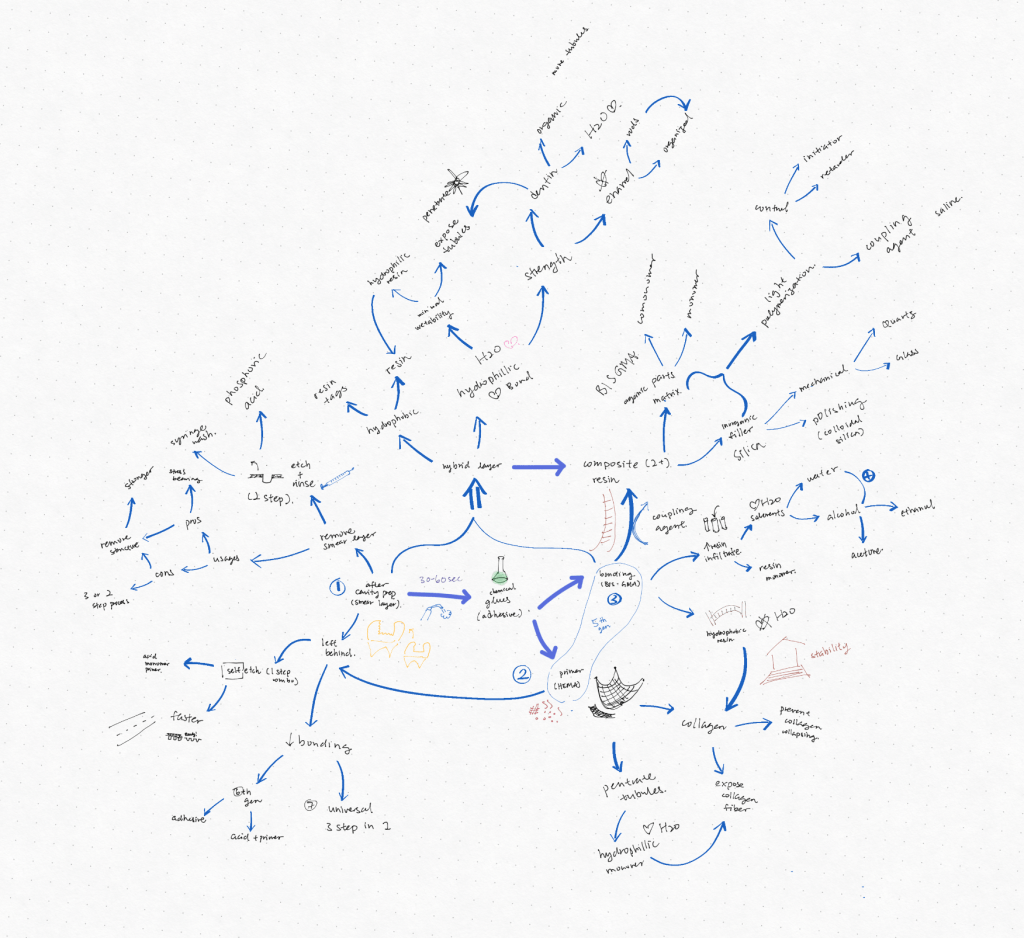
When you go to the dentist, do you know what materials they put on your cavity fillings? Dentists are like construction workers for your teeth. There are specifically designed adhesive systems to bind the filling material onto the surfaces of your teeth.
Two types of adhesive systems help composite bind: self-etch and etch-and-rinse.
The composite contains organic and inorganic components and a coupling agent bringing them together.
- Inorganic filler
- Organic BIS GMA
- Initiators, retarder, and coupler
First, Your Teeth are Prepped.
The cavity is eroded in different shapes and forms when a patient enters the dental clinic. The cavity needs to be reshaped before it can be adequately filled. Just like drilling a hole into a wood plank, a dentist will use a drill to remove the infected dentin and enamel to create a flat surface for the teeth.
Depending on the cavity class, the principles of cavity prep can be changed.
Class 1: Occlusal cavities
Class 2: Occlusal and proximal surface cavities
Class 3: Proximal caries
Class 4: Proximal Caries involving incisor edges
Class 5: Cervical (neck of teeth) caries.
The Teeth are Cleaned With Acid
After the drilling cavity prep, the “sawdust” of the teeth also needs to be cleaned. Otherwise, the adhesive system cannot work in a dirty environment. The layer of dust is called the smear layer.
The agent that can remove the smear layer has erosive characteristics. The two types are etch-and-rinse and self-etch. Imagine cleaning the sawdust and having the choice to wash it off.
Acid etches, or etch-and-rinse, is when the acid is left, not the teeth, to erode the dust and wash it off. The acid bleeds into the tooth structure and creates micropores for bonding. This etching damages teeth structure and bonds deeper because it penetrates the teeth more. Then, a primer will be added next.
There are two sub-divisions of etch and rinse.
- Multi bottle: Acid etch + primer + adhesive
- One bottle: Acid etch + one bottle adhesive
At the same time, self-etch is a combination of primer and acid. The self etch agent is left on the teeth. The acid monomer demineralizes the dentin and creates a thinner primer layer than the etch-and-rinse, which has a less potent effect on destroying the tooth structure.
There are two sub-divisions of self etch
- Two steps: Acidic primer + adhesive
- All in one step: Acid prime and adhesive.
The Hybrid Layer Strengthens the Bond
Dentin and enamel have structural tubules that make the composite difficult to bond to the teeth. To strengthen the bond, the hybrid layer acts as a bridge to the composite. Like in learning, I prime my brain with a knowledge framework and anchor the structure to prior knowledge; the hybrid layer serves the same function. The mixed layer penetrates and interlocks resin tags into the dentinal and enamel tubules.
Dentin has a more irregular, complex, and organic matrix, so compared to the inorganic enamel, it is much harder to bond.
The composite resin is hydrophobic, and the tooth structures are hydrophilic, so there are two parts in the hybrid layer.
- The resin tags and adhesive are hydrophobic.
- There are monomers in this layer that can bond mechanically (amine group in base to the bond with collagen fibers) and chemically (acid carboxyl groups) to the composite and tooth structures.
- The lower hydrophilic is the other part that bonds to the collagen fiber in dentin and enamel.
The Universal Etch
Evaluate the effectiveness of universal adhesive systems compared to other adhesive systems.
In this era of fasted pace and the productivity-obsessed world, the universal adhesive system is time-saving because it is designed to function with etch-and-rinse and self-tech methods. However, this speed has downsides; the hybrid layer may not be firmly fitted in the micropores in the dentin and enamel. In addition, some studies have shown that etch-and-rinse adhesives have better bonding performance because of penetrating deeper.
Other factors that Affect the Bonding Strength
Since the hybrid layer has two parts: hydrophilic and hydrophobic, The hydrophobic adhesive layer part can be disrupted by moisture. The moisture can be controlled with rubber damps or air drying.
Thickness. An adhesive layer cannot be too thick because it won’t be able to penetrate the resin. The hybrid layer thickness will be related to the adhesive layer’s thickness. The adhesive layer cannot penetrate if the mixed layer is thicker.
Evaluate the impact of aging and degradation on the bonding strength of adhesive systems.

Leave a comment