Reading time: 5 minutes
Arguably, thought leaders like Elon Must and Naval Ravikant think the education system is obsolete.
College and schools and the way we think about them come from a time when books were rare
Naval Ravikant
Don’t confuse schooling with education. I didn’t go to Harvard but the people that work for me did.
Elon Musk
But what wins in this era? The ones that are the most responsive to change.
“It is not the strongest of the species that survives, nor the most intelligent that survives. It is the one that is most adaptable to change.”
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
I cannot change the education system. Regardless of the current education system, here’s how you can increase your brain power to make the most of your education.
How does your Brain Process New Information?
Have you ever felt overwhelmed when learning something novel? That is cognitive overload. To understand what is cognitive load, let’s back up a few steps.
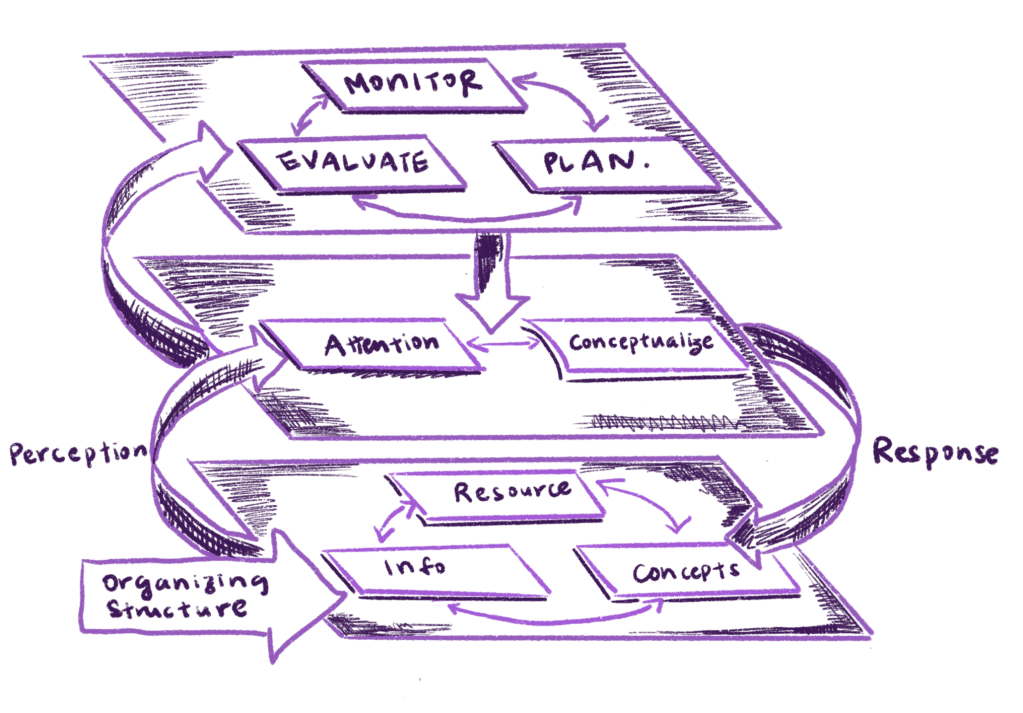
Imagine that your brain is a computer. And reading with your eyes is information coming into your brain. The computer’s memory is where you temporarily store and process the data before it goes into storage. The computer’s processors will evaluate, compare, and analyze the information and decode it. However, the computer’s processor can only process +/- 7 items at once. After processing, you can decide where the information can fit into your existing storage folder systems.
In cognitive psychological terms, the computer’s processor is the working memory; the storage is the long-term memory; your eyes are the sensory memory. Below is a diagram to demonstrate the information processing model in cognitive psychology.

The same situation can happen when you are multitasking when studying. So, please do not multitask.
The cognitive psychologist John Sweller coined the term cognitive load. and it refers to
The amount of information that your working memory can hold at once.
Source
Why is learning in school and real-world different?
There are surprisingly terms for types of knowledge in school teaching and learning a native language at home in educational sciences. The types of knowledge are biologically primary and secondary knowledge.
An example of biologically primary knowledge is learning to speak and listen.
- Biologically primary knowledge is more related to survival
- If humans cannot communicate their needs, they have a lower chance of survival.
- Those skills are learned but are not taught in school.
An example of biologically secondary knowledge is learning to write and read.
- Students cannot discover how to write and read on their own.
- Someone who does not obtain an education will not develop skills to write and read.
- Secondary knowledge is not required to learn for survival.
In evolutionary educational psychology, humans are evolved to learn to find food and speak without much effort, but something like logical reasoning is not.
Finally, John Sweller concluded that cognitive load theory only applies to secondary biological knowledge, but not biological primary knowledge.
Then, if learning is more effortless than finding food, why not use learning abilities in prior knowledge to secondary knowledge?
Furthermore, in France, cognitive psychologists Florence Lespiau and Jean Francois Bonnefon tested the hypothesis. The results revealed that when problems were presented with primary knowledge first, students were more motivated to learn when presenting secondary knowledge first.
How to increase your Brain Power?
Brainpower refers to expanding your endurance to a heavy cognitive load. Like muscles, your cognitive load capacity can be trained.
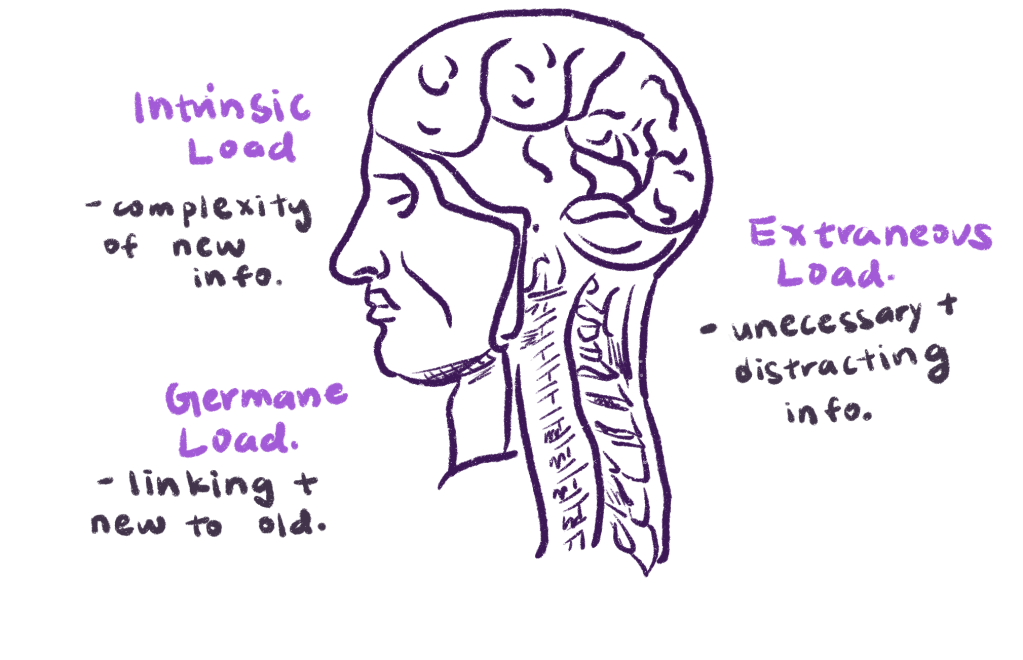
There are three types of cognitive load where you can tackle the information presented to you to increase the amount of information you can process in one sitting. I know the words are getting quite technical but bear with me.
- Germane Cognitive Load.
- A synonym for germane is relevant.
- The definition of germane cognitive load is the mental effort required to put the new information into your existing long-term memory schemas.
- And schemas are just a fancy term for mental models or frameworks. They help you recognize patterns in the real world sorted into categories.
- Extraneous Cognitive Load.
- The way that the information is presented to you.
- Intrinsic Cognitive Load
- The complexity of the new information.
- This isn’t easy to understand the knowledge. The amount of knowledge you have before studying makes a big difference.
So technically, you can “hack” your brain by changing how the information is presented and manipulating the knowledge that suits you the best.
Tips for Increasing Your Endurance on Cognitive Load.
- Build your cognitive schemas and mental models.
- Start with the big picture by drawing a mind map when studying a new topic.
- A big picture leverages intrinsic cognitive loads. It increases the amount of information you can process at once because you are growing your background knowledge in a topic before you start.
- This also decreases the germane cognitive load because you are actively constructing cognitive schemas to your existing memory.
- Once there are more pattern recognition and mentals models built from studying the big picture. Your accuracy and speed of studying will start to increase because you know where to store the new incoming information on your mental bookshelves.
- Practice metacognition.
- Metacognition is planning and monitoring your thinking.
- Plan what you are going to study and set a boundary for your session because I often find my curiosity guiding me to something that is marginally related to the course.
- Chunking the information
- Think of the information you receive as atomic packets that you can manipulate and break apart into meaningful groups.
- A unit of significant chunk has a higher information density than unprocessed or chunked
- Then, start forming groups of information with similar characteristics. The groups and connections can vary widely depending on your antecedent knowledge in the domain.
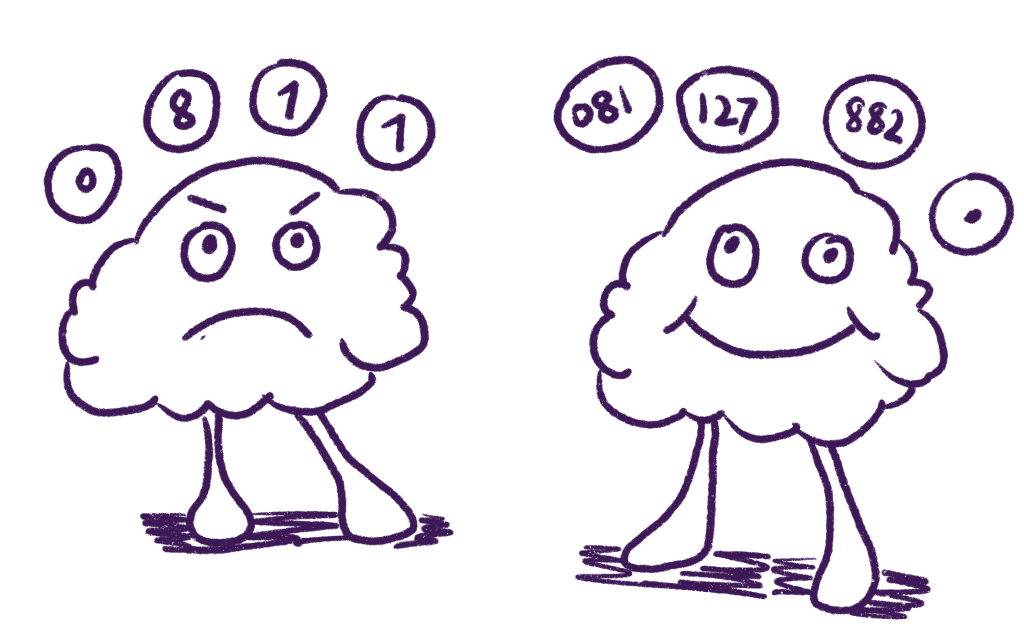
- Writing as a cognition tool.
- Writing allows you to read your thinking on paper to free up your working memory for important tasks.
- Batching in productivity.
- Similar to chunking, you can group similar tasks to decrease the effort in task switching. This decreases the
- For example, you can batch all your admin/paperwork tasks into one hour as a production downtime while blasting some music instead of breaking the flow of your current task to respond to your thoughts.


Leave a reply to Jeffrey Cancel reply